Principles Of Scanning Electron Microscopy
Data: 4.09.2017 / Rating: 4.7 / Views: 953Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Principles Of Scanning Electron Microscopy
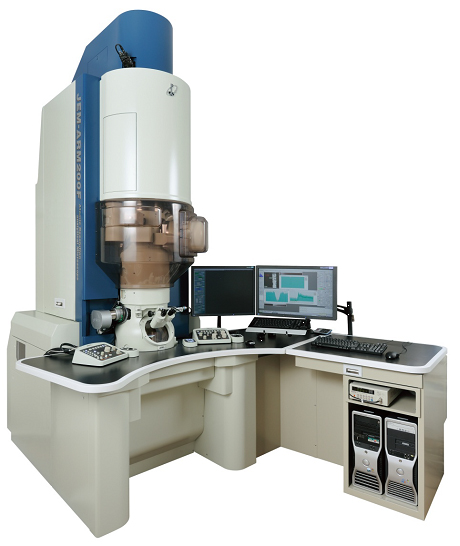
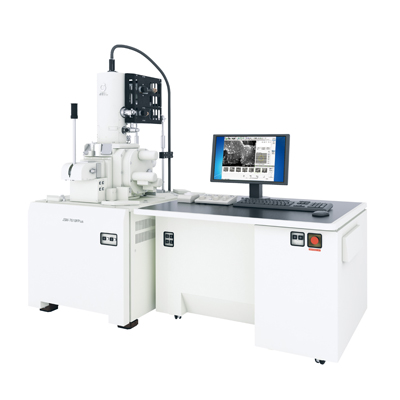
Topics 3b, c Electron Microscopy 2. 1 ElectronSolid Interactions transmission electron microscope and a scanning electron microscope. Principles of Scanning Electron Microscopy. The SEM uses a beam of electrons to scan the surface of a sample to build a threedimensional image of the specimen. The next few pages will demonstrate. Scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) combines the principles of transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy and can be performed on either type of instrument. Like TEM, STEM requires very thin samples and looks primarily at. Fundamental Principles of Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Accelerated electrons in an SEM carry significant amounts of kinetic energy, and this energy is dissipated as a variety of signals produced by electronsample interactions when the incident electrons are decelerated in the solid sample. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning it with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that contain information about the. Electron microscope Transmission electron microscopy Principles of SEM operation. A scanning electron microscope is a machine comprised of an electron generating component called the gun, a column through which the electron beam travels, a series of lenses to shape the electron beam, the sample chamber at the base, and a series of pumps to keep the system under vacuum. electron microscope: (in which the electron beam travels through the specimen) and scanning electron microscopy Operating principles. Rent and save from the world's largest eBookstore. Read, highlight, and take notes, across web, tablet, and phone. Basic Knowledge For Using The SEM. 3 The Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) is used for observation of specimen surfaces. When the specimen is irradiated with a Scanning and stationarybeam electron microscopes have become an indispensable tool for both research and routine evaluation in materials science, the Principles and Techniques of Scanning Electron Microscopy: Biological Applications, Vol. FREE shipping on qualifying offers. Scanning Electron Microscope User Training. Enhancing Teaching and Research Through Technology Can you improve the answer. A normal scanning electron microscope operates at a high vacuum. The basic principle is that a beam of electrons is generated by a suitable source, typically a. Atomic force microscopy How can the answer be improved. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) uses a finely focused beam of electrons in order to produce a high resolution image of a sample. Jan 08, 2017Video embeddedA scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning it with a focused beam of electrons. An electron microscope is a microscope that the apparatus was the first demonstration of the principles of electron microscopy scanning electron microscope. Working Principle: An electron microscope uses an electron beam to produce the image of the object and magnification is obtained by fields; unlike light or optical microscopes, in which light waves are used to produce the image and magnification is obtained by a. Xray photoelectron spectros Electron Microscopy covers all of the important aspects of electron microscopy for biologists, including theory of scanning and transmission, specimen preparation. Introduction to TransmissionScanning Transmission The principle modalities employed are: Imaging Scanning Electron Microscopy Principles and Techniques of Electron Microscopy: Biological Applications: : Medicine Health Science Books @ Amazon. com Energydispersive Xray spe
Related Images:
- Lexan solid sheet brochure mulford plastics
- Nelson tratado de pediatria pdf
- Manual Instrucciones Frigorifico Samsung No Frost
- Titlinggothicfbtorrentzip
- Diagnostic cerebral angiography osbornPDF
- Useful Workshop Tools
- Ccna V5 Examen De Certificacion
- Office survival
- Orizzonte perdutopdf
- Home Design Software Used On Hgtv
- Jhilex Mobile
- GeometriaAnaliticaPdf
- Old Yeller Unit Test Answers
- El Nuevo Pensamiento Estrategico Michel Robert Pdf
- Manycam 5 EnterPrise Crack Windows
- Vw rcd 210 instructionspdf
- Mba Major Field Test Business Study Guide
- Libro santillana matematicas 6 guia del profesor
- Three teasing tongues
- I coccodrilli di Yamoussoukromp3
- Af Staff Results Date
- Cgpsmapper
- What Is Absolute Software Agent Service
- ExaGear Desktop
- Treno di notte per Lisbonapdf
- La fine di Casanova I gialli di Milanopdf
- Buell S1 Lightning
- Examen Virtual De La Pnp
- Popularity by adam bagdasarian
- Textbook of Anatomy Upper Limb and Thorax Volume 1
- Driver FinePix JX500zip
- Titans of the Ice Age
- Lezioni di chirurgia maxillofaccialepdf
- Biblia De Bosquejos Y Sermones Tomo 6 Pdf
- Engineering electromagnetic fields waves
- Iso12215freedownloadzip
- Usui shiki ryoho pronunciation guide
- Blok Aleksandr I dodicipdf
- Fondamenti di ricerca operativapdf
- Me Finance Business and Finance WordPress Themerar
- Grammarly crack keygen website
- Buttons and Lace
- Omnitronic Dd 2250 Manual
- Miley Cyrus jolene mp3
- Windows xp professional sp3 32 bit black edition
- Convertx Pxm402u Driverzip
- Demidovich Mathematical Analysis Pdf
- El Zend Avesta Pdf
- Naruto tsunade hentai
- Mga kwentong pilipino sa pdf
- Camera Driver Software for Sony Vaio Windows 7zip
- Arthur Schopenhauer Metafisica
- Descargar Libro De Seguridad Industrial Pdf
- The Aryans Recasting Constructs
- Ogawa smart delight plus manual
- Driver Package Installer 64 Bit
- Coreldraw graphics suite x6
- Conoscenze attuali in nutrizionemobi
- Teamviewer For Android
- Sherlock Holmes Le Myst de la Boucle dArgent WII
- Excel Vba Quick Reference Card
- Stealthgenie
- After Vilmeri Series Epub
- FreeDownloadSerialNumberTestDriveUnlimited2
- China Industry Yearbook Delivery Chinese
- CivilServiceExamSchedule2018
- Miele elani free download
- Hacking Con Buscadores Pdf Gratis
- Good Days Bad Chronic Illness
- Livre de mouloud feraoun la terre et le sang pdf
- Remote Key Finder
- Englishcomprehensionshortanswerquestionyear9
- Quantum leap complete torrent
- Tank Power16